|
Main Menu | Search | CD Help | Access the Technical Program
Note: Program subject to change without notice
Tuesday, November 6, 2007
207-2
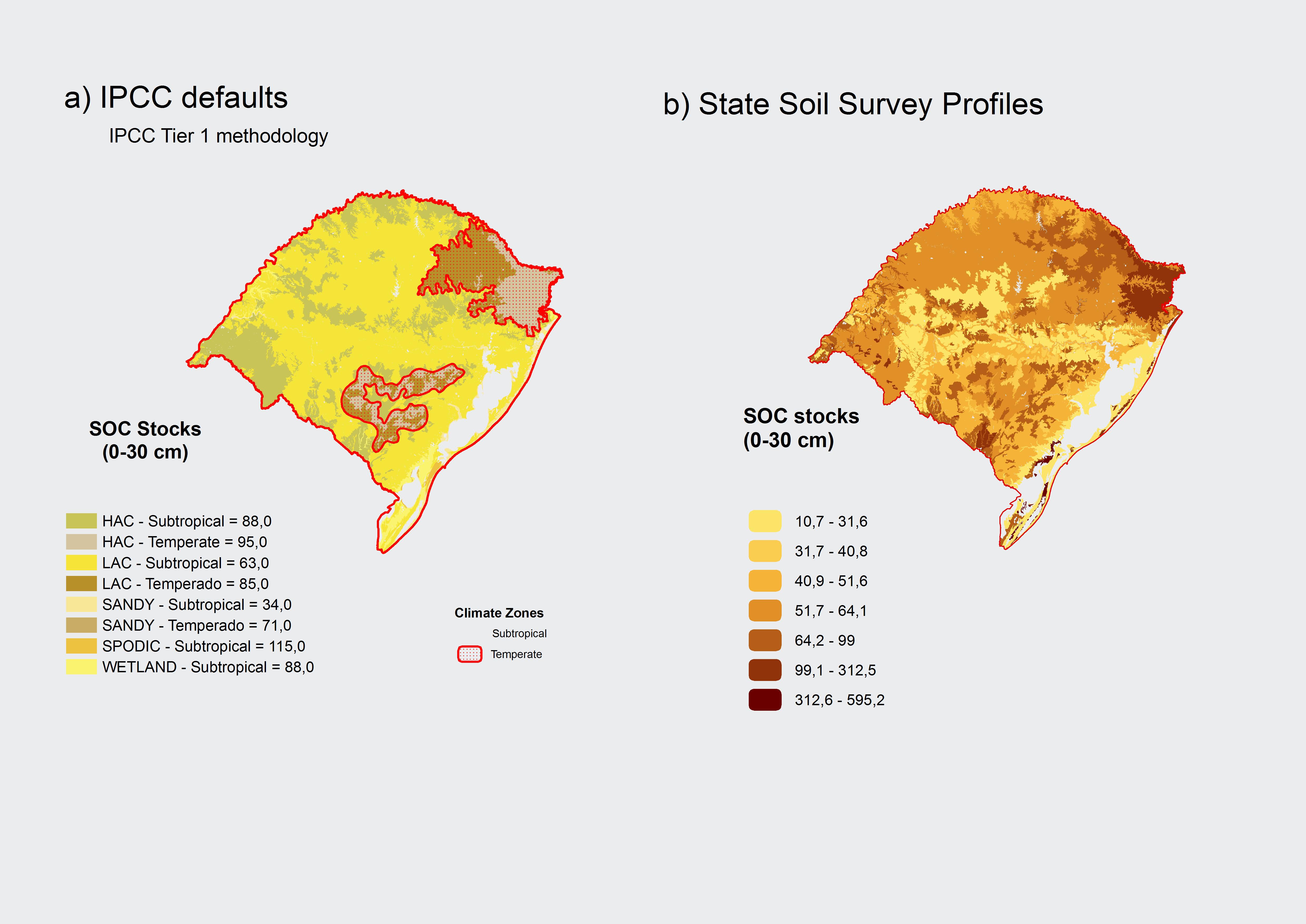
Soil Organic Carbon Stocks of Rio Grande Do Sul, Brazil.
SOIL ORGANIC CARBON STOCKS OF RIO GRANDE DO SUL, BRAZIL
C. G. Tornquist1, C. E. P. Cerri, E. Giasson, J. Mielniczuk.
Soil organic carbon (SOC) plays a fundamental role in the global C cycle: SOC stocks are two times larger than the atmosphere and three times larger than the global biomass C stock. Human intervention in terrestrial ecossystems, especially through intensive agriculture, has led to significant total SOC stocks losses, which contributed to the increase in atmospheric CO2. It has been noted that conservation agriculture practices can turn soils into sinks for atmospheric CO2. Temporal changes in SOC stocks can be evaluated against baseline (original) stocks, i.e. before antropic activity. Original stocks also provide a provisional estimate of potential C sequestration until local soil/mapping unit information is available. We applied geoprocessing tools to estimate original SOC stocks (0 to 30 cm depth) in Rio Grande do Sul (RS) state in southern Brazil. Two recommended IPCC methodologies were tested: one that uses default SOC stock values per soil and climate zone type (Tier 1) and one that applies actual soil profile C data. (Tier 2). The latter was based on existing soil profile database and map (1:1.000.000 scale) of Rio Grande do Sul. We estimated total original RS soil C stocks at 1.942 Pg C (Tier 1 approach) and 1.699 Pg C (Tier 2 approach). Tier 2 results are remarkably similar to an earlier estimate of 1.641 Pg C at coarser-scale (1:5.000.000) [from the Brazilian Greenhouse Gases National Inventory of 2002]. The default Tier 1methodology produced approximately 15% larger total SOC stock estimate. The spatial SOC database created in this study could be further utilized in designing state level SOC stock monitoring programs.